연구/산학
PKNU Research 1000
| Nam Won-il | Develop High-Performance 3D Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Sensor | |||
| 작성자 | 대외홍보센터 | 작성일 | 2025-03-27 |
| 조회수 | 38 | ||
| Nam Won-il | Develop High-Performance 3D Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Sensor | |||||
 |
대외홍보센터 |  |
2025-03-27 |  |
38 |
Pukyong National University Undergraduate Paper Selected as Cover Article in International Journal
- Electronic Engineering Majors Yoon Ji-won and Yoo Hye-im Develop High-Performance 3D Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Sensor
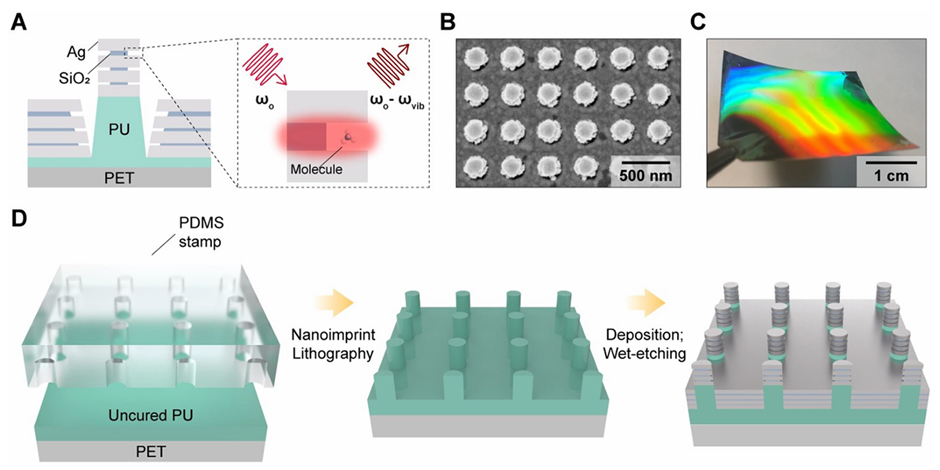
Pukyong National University (President: Bae Sang-hoon) announced that a research paper by Electronics Engineering students Yoon Ji-won (combined master's and doctoral program) and Yoo Hye-im (4th-year student) was published as the cover article in the SCI-level international journal <ACS Applied Nano Materials> (IF: 5.3), Volume 8, Issue 10, in February.
In the cover article titled ‘Plasmonic Nanolamination for High-Performance SERS Substrates Based on Vertically Stacked 3D Multiple Nanogaps’ (supervised by Professor Nam Won-il), the researchers successfully developed a 3D vertical multi-nanogap structure with excellent uniformity and reproducibility using a nanolamination process, providing a new guide for high-performance surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy(SERS) sensors.
SERS (Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy) is a powerful next-generation spectroscopic analysis technique capable of detecting trace amounts of substances, but its practical application has been challenging due to low signal reproducibility and uniformity. The conventional horizontally oriented nanogap structures faced limitations in precision control below 10 nm and difficulties in increasing the density of hotspots. To overcome these issues, the research team introduced a nanolamination technique using a metal-insulator-metal (MIM) stacking structure to create multiple vertical nanogaps, ensuring high-density and uniform hotspots.
The research team maximized the SERS signal enhancement effect by selectively wet etching and removing the insulating layer, exposing the nanogap hotspots to the analyte molecules. Experimental results showed that under optimal etching conditions, the SERS signal enhancement factor reached up to 1.75 × 10^8, demonstrating high uniformity with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of 11% over an area of more than 400 pixels. Additionally, the team successfully created large-area substrates (16 cm²) at a low cost, making them reproducible using nanoimprint lithography.
Professor Nam Won-il (Department of Electronic Engineering, Pukyong National University) stated, "This research presents a new approach that overcomes the limitations of uniformity and reproducibility of conventional SERS substrates. The nanolaminated SERS substrate we developed is expected to be applied in various practical fields such as environmental analysis, biosensors, food safety, and explosives detection."
Meanwhile, Yun Ji-won and Yoo Hye-im achieved this result while conducting research as undergraduate researchers in the Nano-Photonics Lab of Professor Nam Won-il at Pukyong National University's Department of Electronic Engineering. Yun Ji-won is working on environmental sensing research using SERS, while Yoo Hye-im is conducting research on digital SERS and multivariate classification of cancer cells using SERS. <Pukyong Today>
